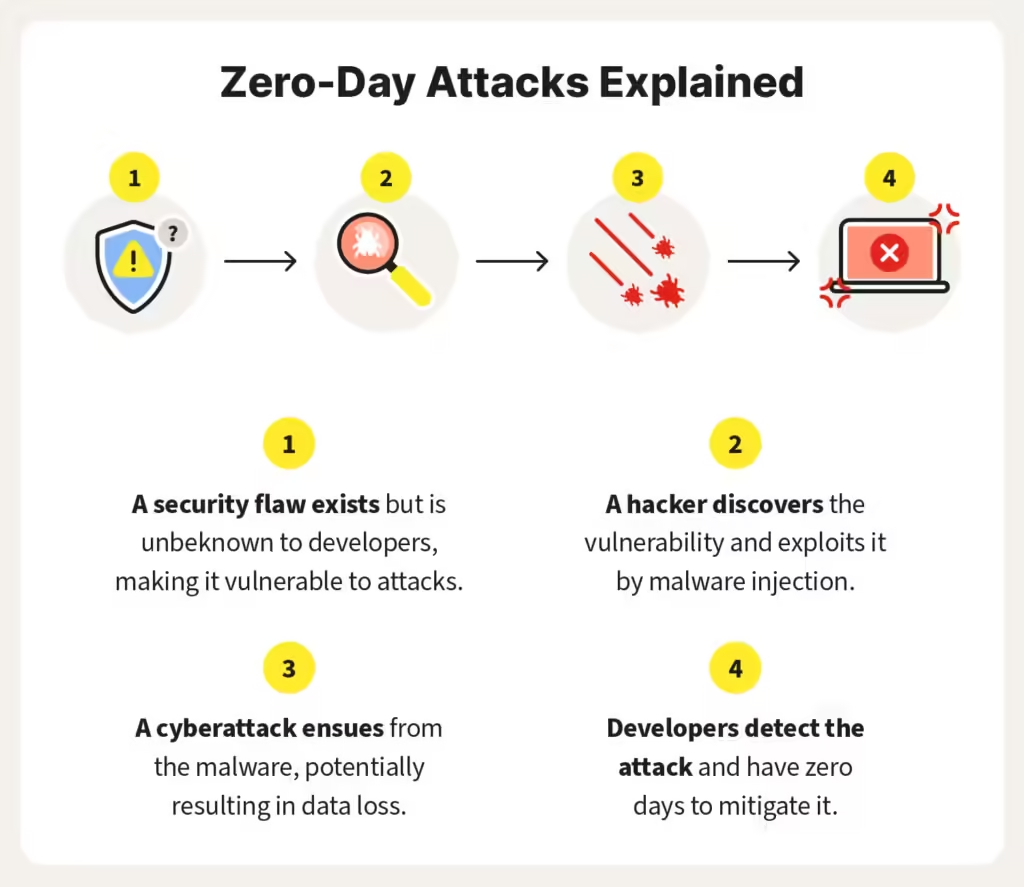
Imagine this: you lock your car door, feeling secure. But unknown to you, a thief has discovered a way to bypass the lock. They use this trick to steal your car. This is exactly what happens in a zero-day attack.
In the digital world, security is paramount. Software developers constantly work to patch vulnerabilities – bugs in their code that hackers can exploit. But what happens when a hacker discovers a vulnerability before the developer? That’s where zero-day attacks come in.
Key Terms to Note
Zero-day vulnerability: A security weakness in software that’s entirely new and unknown to the developer or vendor. Since it’s “zero days old,” there’s no fix (patch) available yet.
Zero-day exploit: The method hackers use to take advantage of the zero-day vulnerability. It’s like the thief figuring out how to bypass your car lock.
Zero-day attack: The actual act of using the zero-day exploit to harm a system. This could involve stealing data, installing malware, or disrupting critical operations.
The Dangers of Zero-Day Attacks
These attacks are particularly dangerous because they catch defenders off guard. Since there’s no patch available, systems remain vulnerable until a fix is developed and deployed. This window of time allows attackers to gain access, potentially stealing sensitive data, compromising entire networks, or causing financial losses.
Staying Safe from Zero-Day Attacks
While there’s no foolproof way to prevent zero-day attacks entirely, you can significantly reduce the risk:
- Keep Software Updated: Software updates often include security patches that address newly discovered vulnerabilities. Regularly installing updates for your operating system, applications, and firmware is crucial. Check out our guide to software updates for more information.
- Use Security Software: A good security suite can help identify and block malicious activity, even if it’s exploiting a zero-day vulnerability. Explore our recommended security software.
- Be Cautious Online: Phishing emails and malicious websites can be used to deliver zero-day exploits. Don’t click on suspicious links or attachments, and be wary of unsolicited downloads. Learn more in our article on phishing prevention tips.
Additional Resources
For further reading on zero-day attacks, you can visit these authoritative sources:
